ARTICLE AD BOX
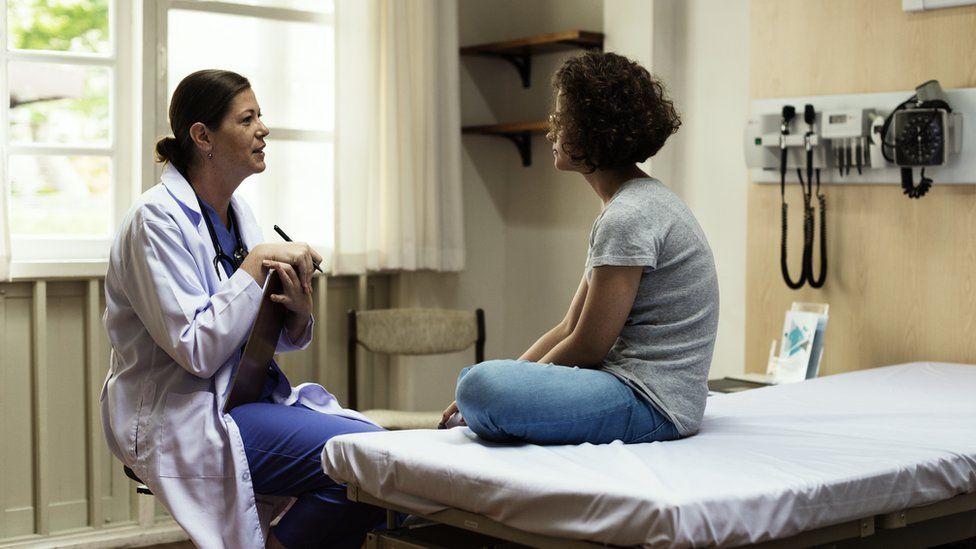 Image source, Getty Images
Image source, Getty Images
Medical students in England will have to pass mandatory training to diagnose and treat female health conditions under plans to improve women's health.
A £10 million investment will fund more mobile breast cancer screening, and new rules should make it easier to compare IVF provision in different areas.
The government said the changes, part of its women's health strategy, were based on responses from 100,000 people.
But critics said more must be done to close the "gender gap" in NHS services.
The government opened a call for evidence in Spring 2021 to collect views on women's health from members of the public, academics, charities and campaigners.
Women in England live on average four years longer than men but spend more of their life in poor health, which can limit their ability to work and participate in day-to-day activities.
Sexism has previously been blamed for a disproportionate rise in gynaecology waiting lists and failings around the prescribing of hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
"Tackling the gender health gap will not be easy - there are deep-seated, systematic issues we must address to ensure women receive the same standards of care as men, universally and by default," said Minister for Women's Health Maria Caulfield.
The government said that individuals responding to the consultation felt there was a lack of understanding among some medical professionals about health conditions which only affect women.
From the 2024/25 academic year, mandatory teaching and assessment specifically relating to women's health will be introduced for all medical students and new doctors.
The government said it also plans to:
- Provide £10 million funding for breast cancer screening to pay for 25 mobile units in areas with low testing rates
- Update guidance around the treatment of severe endometriosis, a debilitating condition which affects one in 10 women where tissue similar to the lining of the womb starts to grow in other places, such as the ovaries and fallopian tubes
- Introduce a pregnancy loss certificate in England, providing legal recognition when a baby dies within the first 24 weeks of pregnancy
- Encourage the expansion of dedicated women's health hubs so maternity, gynaecology and sexual health services can be accessed in a single place
Miriam Levin, health and care programme director at the charity Engage Britain, welcomed "any steps" to tackle health inequalities, but said the government had to ensure that women's concerns would be properly listened to.
"We hear stories of women suffering with a vast range of problems, from endometriosis to menopause, and often feeling as though they're dismissed or not taken seriously by some health professionals," she said.
"The only way this strategy can succeed is for the government to take a fresh approach - by hearing what female patients have to say, then putting their experiences at the very heart of delivering it."
'Postcode lottery' for IVF
Under the plans, there will also be changes to the rules around fertility treatment in England:
- In the future, couples considering IVF should be able to see how NHS provision in their local area compares with other parts of the country.
- It will be possible to access NHS fertility treatment if one half of a couple has had a child in the past, something that has proved difficult in much of England.
- Female same-sex couples will no longer have to pay for artificial insemination at a private clinic to prove they are having difficulty conceiving before being able to access IVF services on the NHS.
Sarah Norcross, director of the fertility charity PET, welcomed the decision to remove some barriers to IVF access but said it was "incredibly disappointing" that there was no plan to tackle the "postcode lottery" of treatment in different parts of England.
"The commitment to improve transparency in relation to the availability of IVF does not equate to giving women the chance to try to have a baby," she said.
Health Secretary Steve Barclay said: "Our health and care system only works if it works for everyone. It is not right that 51% of our population are disadvantaged in accessing the care they need, simply because of their sex."
Related Internet Links
The BBC is not responsible for the content of external sites.

 2 years ago
60
2 years ago
60







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·